Research Review: Cannabidiol's Potential in Reversing Fentanyl Addiction and Reducing Neuroinflammation
A recent study (in mice) concluded that inhaled CBD could alleviate fentanyl addiction and regulate neuroinflammatory responses.
As a holistic mental health and pain clinic, NeuroPain Health is always eager to share the latest research on alternative treatment options for addiction. Today, Dr. Weiner explores a recently published study that concluded that inhaled CBD could alleviate fentanyl addiction and regulate neuroinflammatory responses.
The opioid crisis, particularly the rise in fentanyl addiction, has posed significant challenges for healthcare providers. Fentanyl, a synthetic opioid, is 50 times stronger than heroin and 100 times stronger than morphine, leading to a high risk of overdose and death.
Traditional treatments for opioid addiction often involve medication-assisted therapy (MAT), which has its own set of limitations. Recent research has highlighted the potential of cannabidiol (CBD) in reversing fentanyl addiction and modulating neuroinflammation, offering a promising alternative.
The Study: Cannabidiol and Fentanyl Addiction
The study investigated the effects of inhaled CBD on fentanyl addiction using a conditioned place preference (CPP) model in mice. The study aimed to determine whether CBD could reverse fentanyl addiction and ameliorate associated neuroinflammatory responses.
Methodology
The researchers used male C57BL/6 mice, which were divided into groups and subjected to fentanyl-induced CPP. The mice received either fentanyl or a placebo and were conditioned to associate specific chambers with the presence or absence of the drug. The study employed various methods to assess the impact of CBD on fentanyl addiction and neuroinflammation:
Conditioned Place Preference (CPP): This method evaluates the reinforcing effects of drugs by measuring the time spent in drug-associated chambers.
Behavioral Tests: These included the Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) to assess anxiety-related behavior and the Straub tail reaction to evaluate drug-induced spasticity.
Flow Cytometry and Immunophenotyping: These techniques were used to analyze brain tissue and measure the expression of inflammatory markers in microglia, macrophages, and T cells.
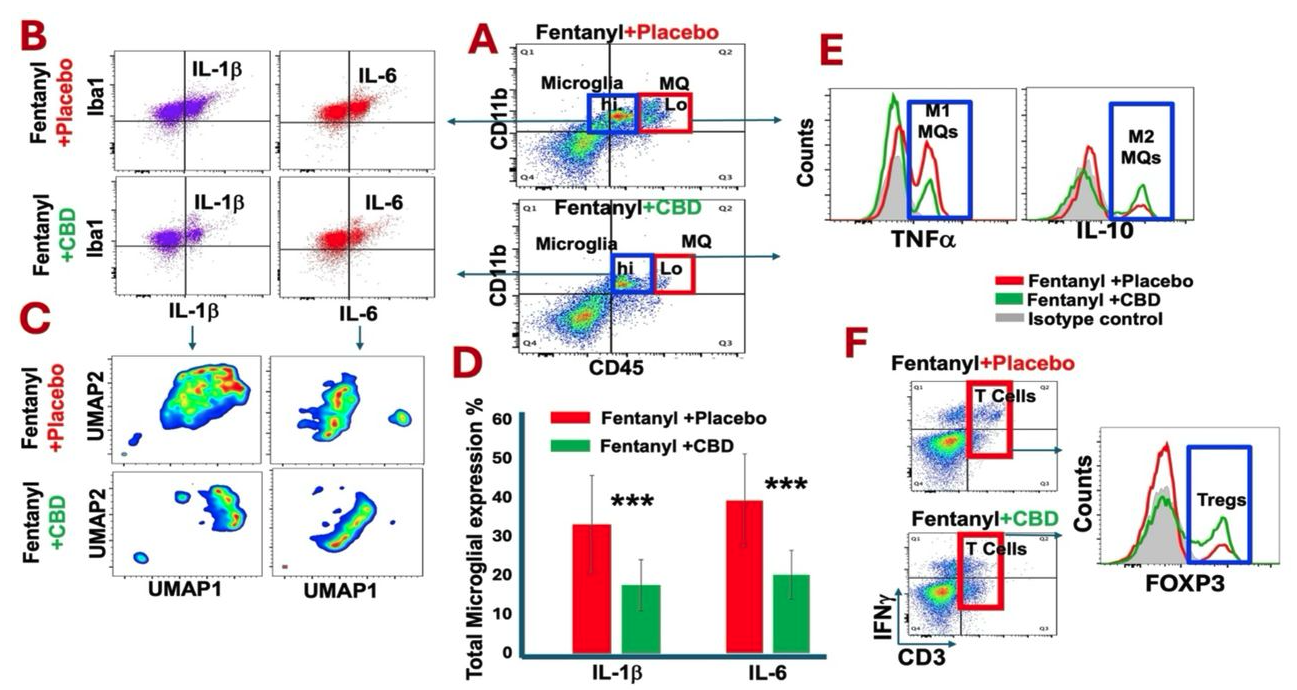
CBD inhalation downregulated fentanyl-induced neuroinflammation. Diagram & Caption via bioRxiv
An assessment of neuroinflammatory signals including microglia, infiltrating macrophages and T lymphocytes was performed using flow cytometry analysis: A) CBD inhalation could enhance counter inflammatory functions of both microglia (CD45loCD11b+Iba1+) and infiltrating macrophages (CD45hiCD11b+ IL-10+) with higher level of IL-10 expression compared to placebo treated group. B) CBD inhalation reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1b and IL-6, by microglia compared to placebo group. C) The analysis of flow cytometry data using the FlowJo software plugin for the algorithm UMAP. The UMAP subtraction analysis revealed numerous spatial clusters with significant differences in IL-1b and IL-6 distribution between fentanyl addicted mice treated with placebo versus CBD treated mice. D) The chart with bargraphs demonstrates the quantified measures for IL-1b and IL-6 expression by microglia with significant reduction in CBD treated compared to placebo group (***p<0.01). E) CBD treatment reduced the type 1 infiltration macrophages (CD45hiCD11b+ TNFa+) while enhanced the type 2 with higher expression of anti-inflammatory IL-10 cytokine. F) CBD inhalation increased the frequency of regulatory T cells (Tregs: CD3+FOXP3+IL-10+IFNg-/lo) with higher expression of IL-10, promoting anti-inflammatory signals.
Key Findings
Reduction in Fentanyl Addiction: CBD inhalation significantly reduced the time mice spent in the fentanyl-associated chamber, indicating a decrease in addiction.
Improvement in Behavioral Symptoms: CBD alleviated abnormal behaviors associated with fentanyl addiction, such as abnormal body curvature and tail stance (S shape).
Reversal of Straub Tail Reaction: CBD treatment reversed the fentanyl-induced Straub tail reaction, a measure of drug-induced spasticity.
Modulation of Neuroinflammation: Flow cytometry revealed that CBD reduced the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, and GM-CSF) and decreased cellular stress and senescence markers in brain tissue.
Rapid Onset of Action
One of the significant advantages of CBD is its rapid onset of action. Unlike traditional anti-inflammatory medications, which can take days or weeks to show effects, CBD can provide quick relief from inflammation and pain. This rapid action is particularly beneficial for patients experiencing severe pain or withdrawal symptoms.
Potential for Long-Term Benefits
While the immediate effects of CBD are well-documented, ongoing research aims to understand its long-term benefits. Preliminary findings suggest that CBD may help reset the body's inflammatory response, leading to sustained improvements in pain and addiction symptoms. However, further studies are needed to fully elucidate these long-term effects.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The implications of these findings extend beyond just addressing fentanyl addiction. CBD’s ability to modulate neuroinflammatory responses offers a new avenue for potentially treating various substance use disorders. Moreover, the non-invasive and relatively non-addictive nature of CBD makes it an appealing candidate for inclusion in broader addiction treatment frameworks.
This study advocates for further exploration into CBD’s role in addiction therapy, advocating for more clinical trials to better understand its efficacy and mechanisms in humans. It underscores an innovative shift towards leveraging immunomodulatory strategies to treat complex drug dependencies, potentially transforming our approach to addiction treatment.
Conclusion
Cannabidiol's ability to reduce inflammation and reverse fentanyl addiction represents a significant advancement in the treatment of opioid addiction and chronic pain. By modulating inflammatory pathways and reducing proinflammatory cytokines, CBD offers a multifaceted approach to managing these conditions. As research continues, CBD's role in treating inflammation and addiction will likely expand, providing new hope for patients with chronic inflammatory conditions and opioid addiction.
For those considering CBD as a treatment option, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure it is administered safely and effectively. Our clinic is dedicated to providing evidence-based treatments and personalized care to help patients achieve optimal health and well-being. Contact us today to learn more about how we can utilize tools such as CBD, ketamine-assisted therapy, and the S.T. Genesis for the treatment of addiction.